インダクタとは何かについて前の記事を読んだことがある方は、次のレベル、インダクタンス式回路とは何かに進んでみましょう。
インダクタが受動素子のリストに追加されたので、直列並列組み合わせの強力なツールを拡張する必要があります。 実用的な回路に見られる直列接続または並列接続された一連のインダクタの等価インダクタンスを見つける方法を知る必要があります。
直列インダクタ
図に示すように、N個のインダクタの直列接続を考えます。(1a)、図に示す等価回路を有する。(1b)。

インダクタには同じ電流が流れています。 <596><2900>インダクタンス式回路にkvlをループに適用すると、
vk=Lk di/dtを代入すると、
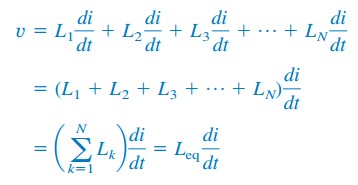

このように,
直列接続されたインダクタの等価インダクタンスは、個々のインダクタンスの合計です。
直列のインダクタは、直列の抵抗とまったく同じ方法で結合されています。
並列インダクタ
ここで、図に示すように、n個のインダクタの並列接続を考えます。(2a)、図中の等価回路を有する。(2b)。 インダクタは、それらの両端で同じ電圧を持っています。

しかし、
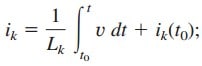
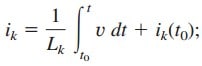

ここで
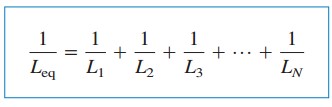
T=t0におけるLeqを通る初期電流i(t0)は、KCLによってt0におけるインダクタ電流の合計であると予想されます。 このように、式による。(5),
![]()
は式に従います。(6),
並列インダクタの等価インダクタンスは、個々のインダクタンスの逆数の合計の逆数です。
並列のインダクタは、並列の抵抗と同じように結合されていることに注意してください。
2つのインダクタを並列に(N=2)すると、式が得られます。(6)となる
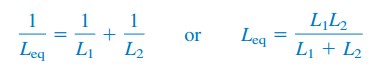
インダクタンス式回路例
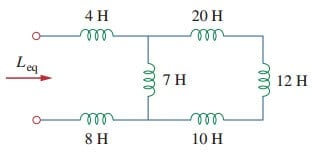
1. 図に示す回路の等価インダクタンスを求めます。(3).
解決策:
10-H、12-H、および20-hのインダクタは直列になっているため、それらを組み合わせると42-hのインダクタンスが得られます。 この42-hインダクタは7-hインダクタと並列になっており、それらを組み合わせることで
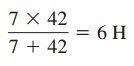
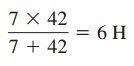
この6-hインダクタは、4-Hおよび8-hインダクタと直列に接続されています。 したがって、,
![]()
2. 図の回路のため。(4),
i(t)=4(2−e−10t)mA. I2(0)=-1mAの場合、
(a)i1(0);
(b)v(t),v1(t),v2(t);
(c)i1(t)およびi2(t)を求めます。

解:<1 9 2 0>(a)からi(t)=4(2−e−1 0t)m A、i(0) = 4(2 − 1) = 4 ママ
Since i = i1 + i2,
![]()
(b) The equivalent inductance is
![]()
Thus,


and


Since v = v1 + v2,
![]()
(c)電流i1は
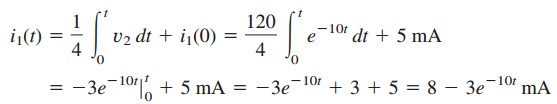
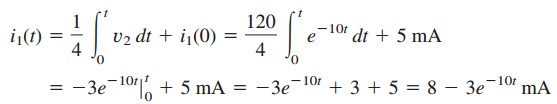
,
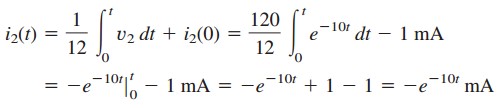
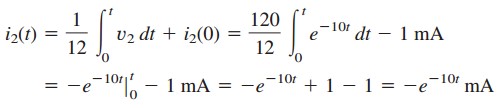
i1(t)+i2(t)=i(t)であることに注意してください。